Severe headache that prevents patients from carrying out activities of daily living
“Patients commonly describe their headache as pressing, explosive with a frontal, retroorbital localization”
High hospital admission rate of 38%
Papilledema (bilateral optic nerve swelling) can be progressive and lead to enlargement of blind spots
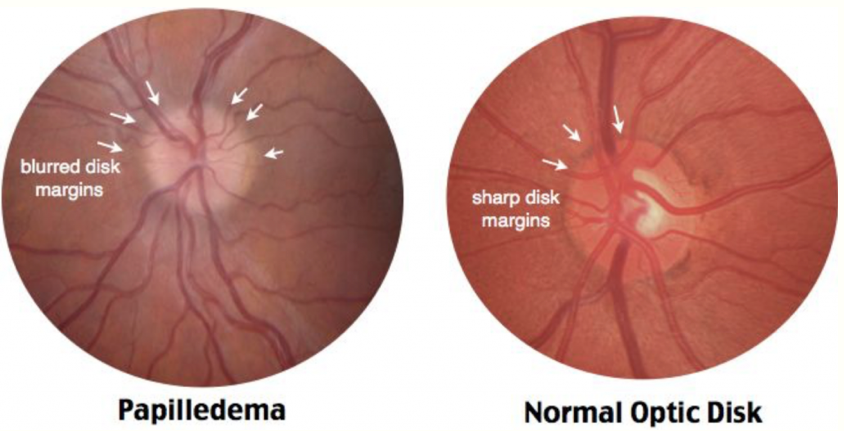
Common visual disturbances include blurred vision, visual obscurations and loss of vision
IIH without Papilloedema (IIHWOP) Diagnostic criteria
Presence of criteria B-E for IIH plus:
Suggestion of possible lIHWOP if:
Presence of criteria B-E for IIH plus:
Diagnostic criteria for IIH (commonly referred to as the Friedman criteria).
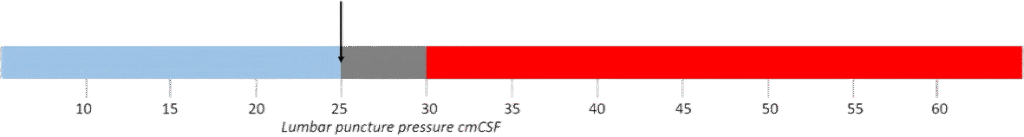
The above graphic illustrates the diagnostic criteria for IIH and IIH without papilledema. Normal lumbar pressure is indicated in the blue area. When lumbar pressure is between 25 and 30 cm of cerebral spinal fluid (the gray area), it can represent normal pressure in some individuals, but can indicate pathologically raised intracranial pressure in other individuals. Measurements in the grey zone need to be interpreted with caution and patients must fit the other criteria for IIH for a diagnosis to be confirmed. Individuals with pressure in the red area have elevated lumbar pressure and have IIH if they meet the above-noted criteria.